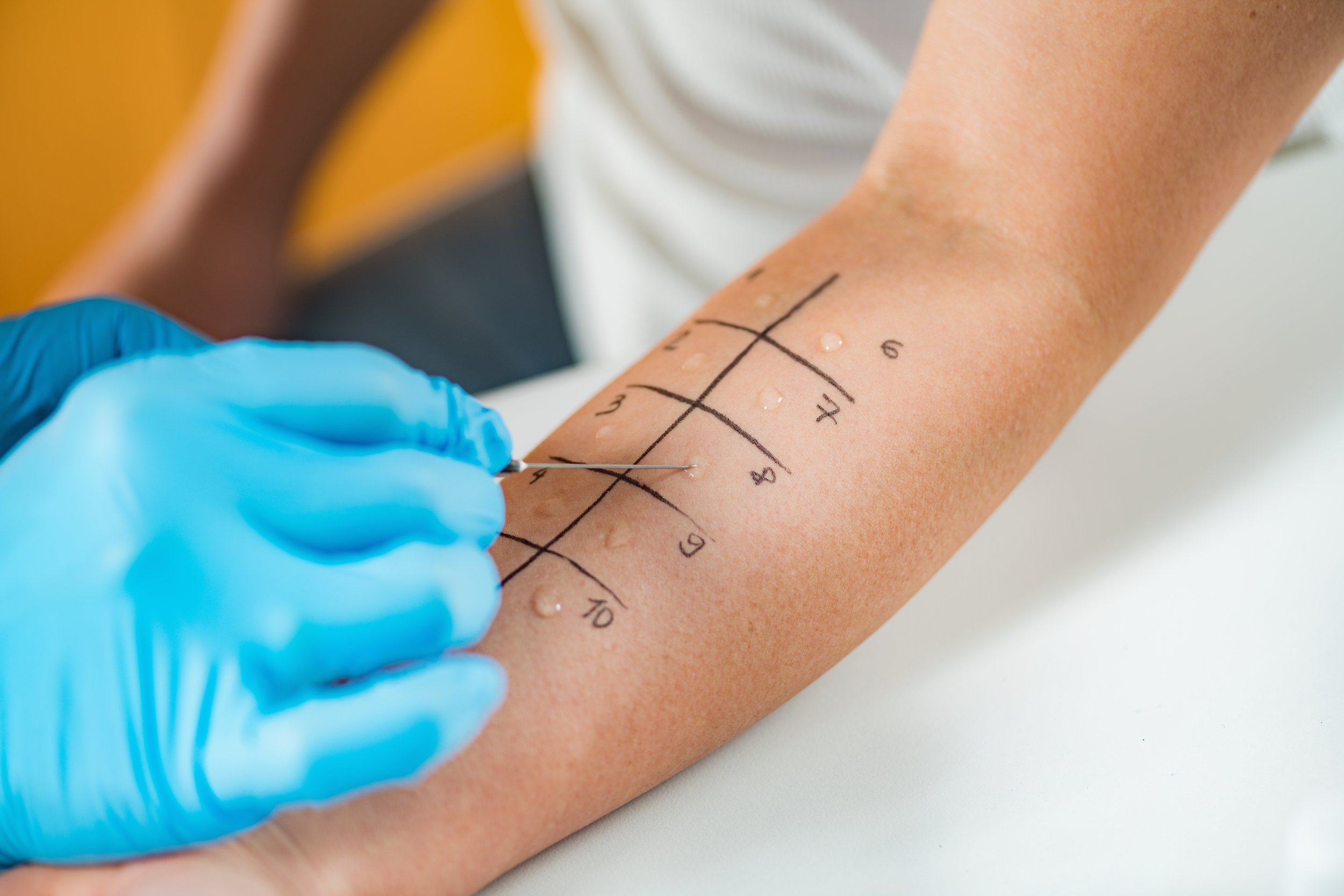
Skin Testing
Skin tests are methods of testing for allergic antibodies called specific IgE. A test consists of introducing a small amount of the suspected allergen into the skin and noting the development of a positive reaction (which consists of a wheal, swelling, or flare/redness). The results are interpreted 15 minutes after the application of the allergen.
Testing can be performed to important Mississippi airborne allergens, foods (peanuts, shellfish, milk, egg, and others), stinging insects (wasps, bees, fire ants, and others), or certain drugs (penicillin, lidocaine).
Types of Skin Tests
Prick Testing
The skin is pricked with a plastic device which has been dipped into an extract of allergen.
Intradermal Testing
Small amounts of an allergen are injected into the superficial layers of the skin.
Patch Testing
A type of test in which allergens are applied to patches and placed on the skin. This type of test does not use needles.
What to Expect
Skin testing generally takes only a few minutes. Prick tests are usually performed on the back but may also be performed on the arms. Intradermal skin tests may be performed if the prick skin tests are negative and are performed on the arms. Positive tests consist of a red, raised, itchy bump and will gradually disappear over a period of 30 to 60 minutes, and, typically, no treatment is necessary for this itchiness. Occasionally local swelling at a test site will begin 4-8 hours after the skin tests are applied, particularly at sites of intradermal testing. These reactions are not serious and will disappear over the next week or so.
Skin testing will be administered at this medical facility with a medical physician or other health care professional present since occasional reactions may require immediate therapy. These reactions may consist of any or all of the following symptoms: itchy eyes, nose, or throat; nasal congestion; runny nose; tightness in the throat or chest; increased wheezing; lightheadedness; faintness; nausea and vomiting; hives; generalized itching; and shock, the latter under extreme circumstances. Please let the physician and nurse know if you are pregnant or taking beta-blockers. Allergy skin testing may be postponed until after the pregnancy in the unlikely event of a reaction to the allergy testing.
Important Things To Remember
1. No prescription or over the counter oral antihistamines should be used 3 to 5 days prior to skin testing. These include cold tablets, sinus tablets, hay fever medications, over the counter allergy medications such as Claritin, Zyrtec, Allegra, Actifed, Dimetapp, Benadryl, and over-the-counter sleep medicines such as Tylenol PM. Prescription antihistamines such as Clarinex, Xyzal, hydroxyzine, nasal antihistamines such as Patanase, Dymista, Astelin, and ocular antihistamines such as Pataday or Optivar should also be stopped at least 5 days prior to testing. If you have any questions whether or not you are using an antihistamine, lease please ask the nurse or the doctor. In some instances a longer period of time off these medications may be necessary.
2. Prescribed medications such as amytriptyline hydrochloride (Elavil), doxepin (Sinequan), and imipramine (Tofranil) are potent antihistamines and should be discontinued at least 2 weeks prior to receiving skin testing after consultation with your physician. Please make the doctor or nurse aware of the fact that you are taking these medications so that you may be advised as to how long prior to testing you should stop taking them.
3. You may continue to use your intranasal allergy sprays such as Flonase, Rhinocort,
Nasonex, Nasacort. Omnaris, Veramyst, Zetonna, and Qnasl.